Environmental Problems of Rural Areas in India
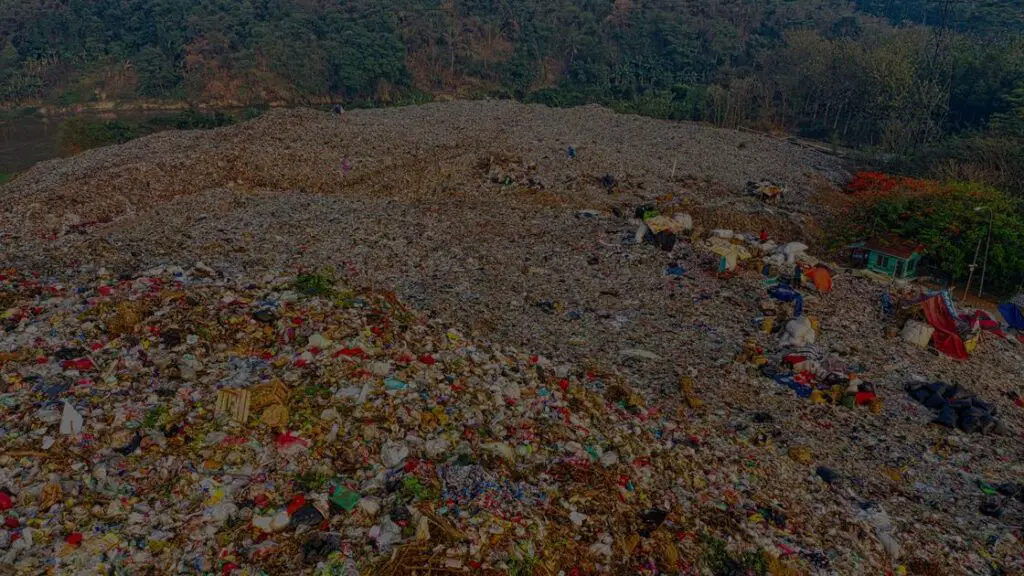
India is a diverse and beautiful country, with many rural areas but sadly that are facing many environmental problems due to various hazardeous changes that are taking place. These problems include water and land pollution, waste management, deforestation, depletion of resources, climate change and more. This blog will help you understand the top environmental problems of rural areas in India. By reading this blog, we hope to raise awareness and inspire you to take action towards a greener and better future. Air pollution Air pollution is a major concern in India, making the air dirty and unsafe to breathe. Various reasons that are responsible for Air pollution, One the top most environmental problems of rural areas in India Air Quality index is the metrix used to determine how good or bad the cities air is Breathing in this polluted air can make people sick, especially children and older adults who are more vulnerable. The India’s polluted cities based on the Air quality Index Rank State, City AQI- IN 1 Karnataka, Gadag 837 2 Himachal Pradesh, Baddi 365 3 Delhi, Delhi 315 4 Telangana , Hyderabad 283 5 UP, Hapur 273 6 UP, Muzaffarnagar 265 7 Rajasthan, Bhiwadi 264 8 UP, Greater Noida 250 9 Haryana, Faridabad 238 10 UP, Noida 231 To improve the situation, it’s crucial to explore alternative farming techniques that don’t involve burning crops and to adopt cleaner cooking methods. Government can play an important role by implementing regulations to limit pollution from industries and outdated vehicles. Water pollution Water pollution is a significant environmental problems of rural areas in India, mainly due to industrial and agricultural activities, as well as improper waste disposal, farms introduces harmful chemicals into water sources, while untreated sewage and plastic waste further contaminate them. This pollution not only threatens human health but also harms marine life and ecosystems. To tackle water pollution, we need strict regulations on industrial discharge and promotion of sustainable farming practices. Investing in better infrastructure of waste water treatment facility is also crucial. Waste management: Rural communities often lack proper waste disposal systems, leading to piles of garbage accumulating in unsightly heaps. This not only damages the natural beauty but also poses health risks for people and wildlife. To address this issue, innovative solutions are needed. Community-led initiatives, such as recycling projects and composting programs, can help reduce waste. Additionally, raising awareness about responsible waste management is crucial. By encouraging practices like reducing, reusing, and recycling is the best way. Deforestation Deforestation silently erodes the lush greenery that defines major environmental problems of rural areas in India, posing a grave threat to its ecosystems. Impact on Biodiversity: As trees vanish, countless plant and animal species lose their habitat, endangering biodiversity and disrupting delicate ecosystems. Soil Erosion and Water Scarcity: With trees gone, soil becomes vulnerable to erosion by wind and water, leading to land degradation and exacerbating water scarcity. Climate Change: Deforestation contributes to climate change by releasing stored carbon dioxide, intensifying global warming and its adverse effects. hence there are ways to stop deforestation. Soil Degradation There’s a problem lurking underground soil degradation. The way we farm, using lots of chemicals and artificial fertilizers constantly digging up the soil which is making the soil weaker. This means our crops might not grow and give the good freshness, and we have to use more . Also, the soil that gets washed away can make our water dirty and make climate change worse. But there’s good news! If we start farming in a more eco-friendly way, like not digging up the soil so much and using organic fertilizers, we can help the soil become healthy again. Falling groundwater table The water stored underground is disappearing fast. More and more people are using water, like for farming and industry, and they’re taking too much from below the ground. This is causing the water underground to drop quickly, making it tough for farmers to grow crops. It’s also causing fights between villages over who gets what’s left. How We Can Help? But there’s hope! We can do multiple things to save water smartly. Like collecting rainwater when it falls and using it to water plants. Also, we can find better ways to water crops without using too much water. Governments can also pitch in by making rules to stop folks from taking too much water from underground. It’s important for all of us to team up and save water. Public Health Concerns in Rural India In the beautiful countryside of India, there are serious problems affecting both the people and the land. Issues like dirty water, bad waste management, and cutting down trees are making things worse. These problems are not just harming nature but also making people sick. To fix these problems, we need to work together. We can start by making sure everyone has clean water to drink and teaching better ways to farm without hurting the land. We also need to manage waste better to keep our air clean and our communities healthy. By teaming up and focusing on public health, we can make rural India a safer and happier place for everyone. The Fragility of Ecosystems Our natural world is facing a hidden danger: the loss of resilience in ecosystems. This means our environment is struggling to bounce back from problems like pollution and habitat loss. When ecosystems lose their strength, it hurts biodiversity, disrupts essential processes, and makes it harder for people to thrive. Ecosystems need to stay strong to support life and provide resources like clean water and fertile soil. But factors like cutting down forests and polluting rivers are making them weak. Climate change makes things worse by bringing more extreme weather. Why It Matters: When ecosystems can’t cope, it affects everything from farming to drinking water. Communities suffer, and poverty and hunger can get worse. What We Can Do: We need to protect natural areas, plant more trees, and use land wisely. By taking care of nature, we’re taking care of ourselves and
Environmental Problems of Rural Areas in India Read More »